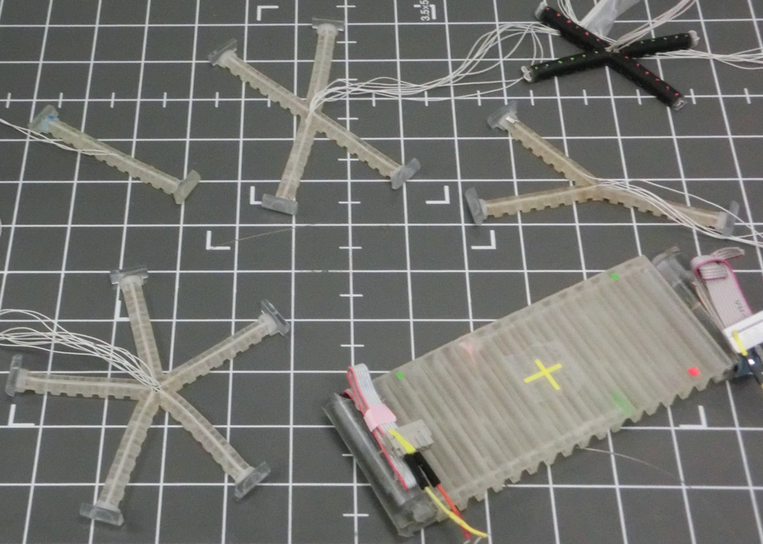
Soft Robotics
What are soft materials and why use them with robots?
Soft materials are "a bulk or composite collection of matter that undergoes deformations of similar or greater magnitude than the deformation of the environment, either plastically or elastically, within the force regime applied by its environment." [Discussion - LINK]
Soft materials in robots allow them to be adaptable by withstanding impact, temporarily store energy and deform to desired profiles. Additionally, the ability of soft materials to change dimensions (e.g. a 3D soft ball can be stretched into a 2D sheet or a 1D rod) make them a suitable candidate for being incorporated into robots moving in unstructured environments. I pursue research design and control of terrestrial soft robots with foreseen applications of exploration and search & rescue tasks in unstructured and semi-structured environments (e.g. natural disasters).
Soft materials are "a bulk or composite collection of matter that undergoes deformations of similar or greater magnitude than the deformation of the environment, either plastically or elastically, within the force regime applied by its environment." [Discussion - LINK]
Soft materials in robots allow them to be adaptable by withstanding impact, temporarily store energy and deform to desired profiles. Additionally, the ability of soft materials to change dimensions (e.g. a 3D soft ball can be stretched into a 2D sheet or a 1D rod) make them a suitable candidate for being incorporated into robots moving in unstructured environments. I pursue research design and control of terrestrial soft robots with foreseen applications of exploration and search & rescue tasks in unstructured and semi-structured environments (e.g. natural disasters).
RoboSoft 2020
|
Motor Tendon Actuated
|
|
|
|
Publications
|
|
P18. A. N. Mahendran, C. Freeman, A. Chang, M. McDougall, P. Vela and V. Vikas . "Multi-gait Locomotion Planning and Tracking for Tendon-actuated Terrestrial Soft Robot (TerreSoRo)." 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2023). [Article Link, arxiv, Youtube Video]
|
P17. N. Jeong, W. Lee, S. Jeong, A. N. Mahendran and V. Vikas, "Background material identification using a soft robot", Electronics 2024. [Article Link].
|
|
P16. H. Bezawada, C. Woods and V. Vikas, "Shape reconstruction of soft manipulators using vision and IMU feedback'", IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2022. [Article Link, YouTube Video].
|
P15. H. Bezawada, C. Woods and V. Vikas "Shape Estimation of Soft Manipulators using Piecewise Continuous Pythagorean-Hodograph Curves", American Controls Conference (ACC), Jun 2022 [Article Link].
|
|
P14. C. Freeman, M. Maynard and V. Vikas "Topology and morphology design of spherically reconfigurable homogeneous Modular Soft Robots (MSoRos)", Soft Robotics [arxiv, Article Link, Youtube Video].
|
|
|
P13. A. Chang, C. Freeman, A. N, Mahendran, V. Vikas and P. Vela, "Shape-centric Modeling for Soft Robot Inchworm Locomotion", 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2021) [10.1109/IROS51168.2021.9636695].
|
P12. N. Kastor, R. Mukherjee, E. Cohen, V. Vikas, B. Trimmer, and R. White, "Design and Manufacturing of Tendon-Driven Soft Foam Robots". Robotica, May 2019. [DOI:10.1017/S0263574719000481]
P11. M. Tanouye, V. Vikas, “Surface identification using terrestrial soft robots”, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Soft Robotics, April 2018 [DOI:10.1109/ROBOSOFT.2018.8405366][Link]
P10. M. Tanouye, V. Vikas, “Surface Identification inspired by reinforcement learning using soft robots”, ASME Early Career Technical Conference, Nov 2017 [Link]
P9. N. Kastor, V. Vikas, E. Cohen and R. White, "A Definition of Soft Materials for use in the design of robots", Soft Robotics, Soft Robotics. September 2017, 4(3): 181-182. [DOI:10.1089/soro.2017.29012], [Link]
|
|
P8. V. Vikas, E. Cohen, R. Grassi, C. Sozer and B. Trimmer, "Design and locomotion control of soft robot using friction manipulation and motor-tendon actuation", IEEE Transactions on Robotics, Aug 2016 [DOI:10.1109/TRO.2016.2588888]
|
P7. V. Vikas, T. Umedachi and B. Trimmer, “Softworms: A New Development Platform for Design and Control of Deformable Robots”, Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, Jan 2016 [DOI:10.1088/1748-3190/11/2/025001]
P6. N. Kastor, M. Hill, V. Vikas, R. White and B. Trimmer, "Semi-Autonomous Soft Robotic Platform for Terrestrial Locomotion'', New Frontiers and Applications for Soft Robotics, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Oct 2015. [POSTER]
|
|
P5. V. Vikas, P. Grover and B. Trimmer, “Model-free control of multi-limb soft robots”, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Oct 2015. [DOI:10.1109/IROS.2015.7353509], [arXiv]
|
P4. V. Vikas, P. Templeton and B. Trimmer. "Design and control of a soft, shape-changing, crawling robot". [arXiv]
P3. E. Cohen, V. Vikas, B. Trimmer and S. McCarthy “Design methodologies for soft material robots through additive manufacturing, from prototyping to locomotion”, ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conference, Aug 2015. [DOI:10.1115/DETC2015-47507]
P2. V. Vikas, P. Grover and B. Trimmer, "Model-free control framework for multi-limb soft material robots", 7th International Symposium on Adaptive Motion of Animals and Machines, June, 2015.[POSTER]
P1. T. Umedachi, V.Vikas and B. Trimmer, "Highly Deformable 3-D Printed Soft Robot Generating Inching and Crawling Locomotions with Variable Friction Legs'', IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nov 2013. [DOI:10.1109/IROS.2013.6697016]